HIGHLIGHTS
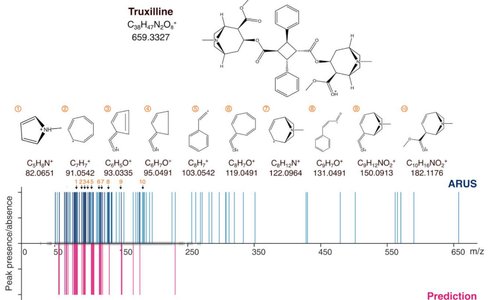
SingleFrag: a deep learning tool for MS/MS fragment and spectral prediction and metabolite annotation
Brief. Bioinf. - July 11, 2025
Metabolite and small molecule identification via tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) involves matching experimental spectra with prerecorded spectra of known compounds. This process is hindered by the current lack of comprehensive reference spectral libraries. To address this gap, we need accurate in silico fragmentation tools for predicting MS/MS spectra of compounds...
Probabilistic alignment of multiple networks
The network alignment problem appears in many areas of science and involves finding the optimal mapping between nodes in two or more networks, so as to identify corresponding entities across networks. We propose a probabilistic approach to the problem of network alignment, as well as the corresponding inference algorithms. Unlike...
Human mobility is well described by closed-form gravity-like models learned automatically from data
Modeling human mobility is critical to address questions in urban planning, sustainability, public health, and economic development. However, our understanding and ability to model flows between urban areas are still incomplete. At one end of the modeling spectrum we have gravity models, which are easy to interpret but provide modestly...
OUR RESEARCH
Complex Systems
Cells, ecosystems and economies are examples of complex systems. In complex systems, individual components interact with each other, usually in nonlinear ways, giving rise to complex networks of interactions that are neither totally regular nor totally random. Partly because of the interactions themselves and partly because of the interaction's topology, complex systems cannot be properly understood by just analyzing their constituent parts.
Data Science
Humans generate information at an unprecedented pace, with some estimates suggesting that, in a year, we now produce on the order of 10^21 bytes of data, millions of times the amount of information in all the books ever written. Processing this "data deluge", as some have called it, requires new tools and new approaches at the interface of statistics, statistical and machine learning, network theory and statistical physics.
Multidisciplinarity
Our goal is to push forward the boundaries of science. We are interested in addressing fundamental questions in all areas of science including natural, social and economic sciences. We put a special emphasis in the development of tools that aid scientific discovery through understanding and quantification of a specific phenomenon. To this end we have assembled a multidisciplinary team and have established solid collaborations with experts in biology, social sciences, ecology and economics.